Optocoupler and Flyback diode in relay circuits
Flyback diode
In relay circuits, a flyback diode is a PN junction diode which is connected across the relay coil in reverse bias to the polarity of the supply voltage. It is connected to discharge the surge voltage or spike induced across the relay coils during switch off or de-energizing of the relay.
The relay coil induces an emf with respect to the rate of change of current. If the circuit is opened using a mechanical switch then it results in a small electrical arc, but in switching using transistors or similar semiconductor devices this voltage surge will damage the components. So, in order to avoid this, a flyback diode is connected across the coil. A flyback diode becomes forward bias during the de-energizing of the relay. Hence it can act as a short circuit across the coil terminals and prevent voltage surge.
Optocoupler
An optocoupler is a device that electrically isolates two circuits and couples them by transferring signals by means of light.
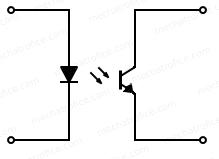
Optocoupler arrangement with IR diode & Phototransistor
The purpose of using an optocoupler with relay-driven circuits is to ensure complete electrical isolation. This is mainly used in outputs taken from the digital pins of microcontrollers or similar sensitive components to eliminate voltage spikes and all the possible chance of electric contact with the external circuits.
Also, optocouplers prevent an electric connection between an external circuit that operates at different voltage levels than the I/O pin voltage.
In the optocoupler circuit, it doesn’t require common ground between the external circuit. The isolated ground can eliminate the noise coupling between the signal output and the relay coil.