Differences Between Neutral, Earth and Ground
Earth, Ground and Neutral all three are similar to each other but often confused or referred one as other. Still, it has the difference to term it separately as they serve for different purposes.
Earthing
An earthing connects specific electrical installation parts with the earth surface which is mainly intended for safety purposes. It is usually connected to the earth by inserting metallic electrodes deep inside to the earth. Earthing is essential for human safety and protection of types of equipment. Also Proper earthing is required for the safety of overall wiring and operation of safety devices such as ELCB, various earth fault relays etc.
An earth line does not carry current under its normal operation; it carries current only during the fault condition. When a fault is present earthing conducts the fault current in the metal parts safely to the ground. And thereby it helps to minimize the risk of an electric shock that might be received while touching a metallic body of the device.
Earthing provides a safe conductive path for the isolated metal parts, which makes a low resistive conductive path between the electrically charged points and earth conductive surface. Hence, it maintains an extremely low potential between the charged part and earth, which is not enough to cause a considerable amount of current flow through a human body or something alike.
For proper functioning the earth line should have very low resistance, that is the conductors should have good conductivity. It should have the ability to dissipate the high amount of fault current. Also good corrosion resistance.
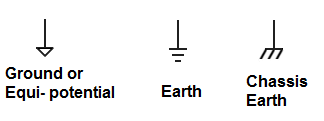
In wiring systems, Green wires are used as earth line. Also in wiring diagrams, the earth line is represented with green color.
Grounding
A grounding can be considered as an equipotential point of the electrical circuit. That is the point which has zero potential with respect to other points which has either positive or negative potential. Unlike from earthing the ground carries current under normal condition.
A point in a circuit which is considered to be ground may or may not be earthed. It can be either chassis earthed (earth terminal connected to the body or metallic chassis of the device); which provides an electrical connection between all the ground points of the circuit which ensures an equal potential or uniform reference voltage at the points connected to chassis. Or ground can be considered as the midpoint of voltage divider networks. That is an exact half of the potential difference between positive and negative potential or peak to peak voltage.
A grounding can be referred similarly to the grounding of neutral point of a star connected transformer, the center tap of a single phase transformer, etc. It is essential to provide grounding for the various function of equipment such as for monitoring battery balance, taking reference voltage, etc.
Neutral
A neutral is a return pathway of current which carries the current back to the source. A neutral line is essential to complete a circuit. Under the no-fault condition, a neutral line and phase line carries an equal amount of current.
If the incoming phase current and neutral current are not the same, it indicates a fault condition resulted due to the leakage of current through some other alternate path. It is often connected to earth in order to avoid isolation of neutral line.
The black color is used for neutral wires and represent it in diagrams.
What is different between Earth & Neutral??
Neutral is a return path for current, which always carries current in normal condition.
Earth is a low resistance path for leakage current. It carries current only during fault conditions. Earthing is for safety purposes to discharge the fault current to the earth. Touching metals parts are earthed to prevent electric shock if any fault contact with the phase or insulation breakdown occurs.
Very good material
how we can fix the ground on the earth’s surface.